In a rapidly evolving world, innovative approaches augment the traditional classroom methods that prepare students for real-world challenges. Project-Based Learning (PBL) is one such approach that empowers students to take charge of their learning through hands-on, collaborative projects. By immersing students in projects that address real-world problems, Project-based learning for schools fosters critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and creativity.
PROJECT BASED LEARNING FOR SCHOOLS
What is Project-Based Learning For Schools?
Project Based Learning (PBL) is an educational approach that places students at the center of their learning journey. In PBL, students engage in in-depth projects around real-world problems or questions. This approach emphasizes inquiry, collaboration, and self-directed learning. Critical characteristics of PBL include:
- Exploration of open-ended questions or problems
- Active engagement in research and investigation
- Application of knowledge to create meaningful solutions
- Collaboration among students to share ideas and insights
- Integration of various subjects and skills to address complex issues
PBL deepens students’ understanding of content and equips them with essential skills for future endeavors.
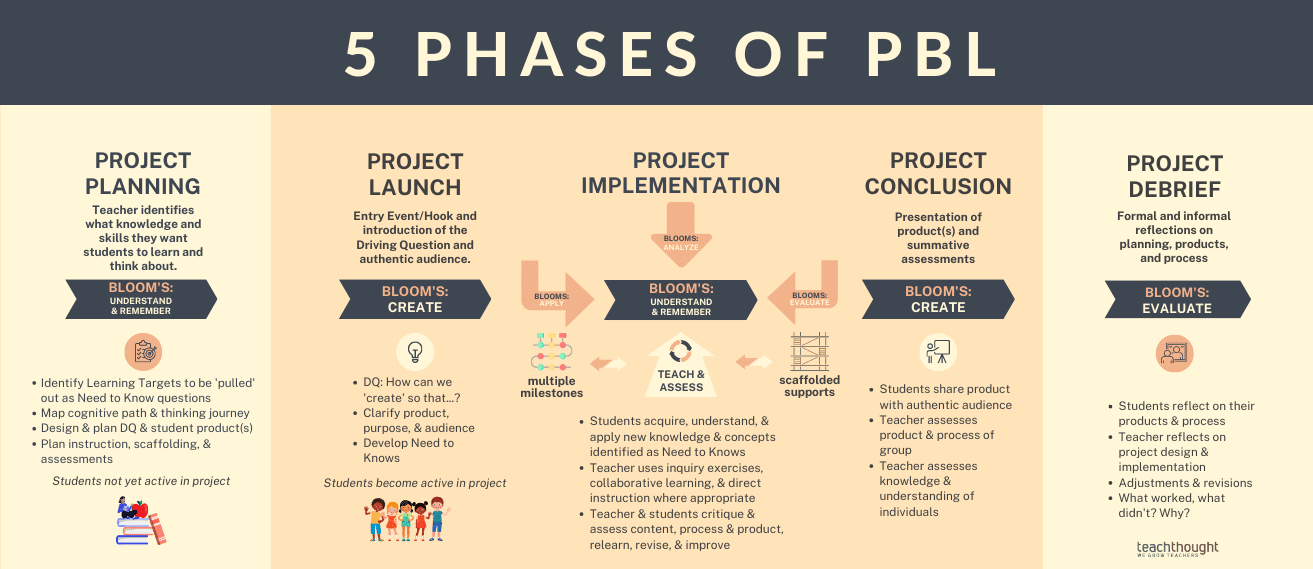
Steps To Implementing Project-Based Learning
Implementing PBL involves a structured process guiding students through the project cycle. Here’s an overview of the steps:
- Identifying the Project Topic: Select a relevant and engaging topic that aligns with curriculum goals and sparks students’ curiosity.
- Defining Goals and Learning Objectives: Set clear objectives to guide the project and determine what students should learn and achieve.
- Planning and Designing the Project: Include the timeline, resources, and assessment criteria.
- Research and Investigation: Encourage students to explore the topic, conduct research, and gather information from various sources.
- Creating a Project Plan or Proposal: Have students outline their project approach, detailing how they will tackle the problem or question.
- Execution and Implementation: Students work collaboratively to develop solutions, applying critical thinking and creativity.
- Reflection, Assessment, and Presentation: After completing the project, students reflect on their learning, assess their outcomes, and present their findings to their peers and instructors. Each step offers opportunities for students to take ownership of their knowledge and develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Benefits of Project-Based Learning:
Project Based Learning offers numerous benefits to both students and educators:
- Enhanced Critical Thinking: PBL encourages students to analyze information, solve problems, and think critically.
- Collaboration and Communication: Students work in teams, improving their communication and teamwork skills.
- Creativity and Innovation: PBL sparks creativity as students design unique solutions to real-world challenges.
- Student Engagement: Projects are engaging, motivating students to become active participants in their learning.
- Real-world Relevance: PBL connects classroom learning to real-life situations, making education more meaningful.
- Preparation for the Future: PBL equips students with skills they’ll need for success in their future careers and endeavors.
Resources & Tools
Exploring Project Based Learning (PBL) can be an enriching experience for educators and learners alike. To help you dive deeper into the world of PBL, here are some valuable resources and tools to enhance your understanding and implementation:
Websites:
- Buck Institute for Education (BIE): A leading resource for PBL, offering project ideas, planning tools, and professional development resources for educators.
- Edutopia – PBL: An online hub with articles, videos, and examples of successful PBL projects, along with tips and strategies for effective implementation.
Online Platforms:
- PBLWorks: Provides various resources, professional development opportunities, and a project library for educators interested in implementing PBL.
- Google for Education: Offers tools like Google Drive, Google Docs, and Google Slides for collaborative project work, research, and presentation.
Online Courses and Workshops:
- PBL University: An online platform offering courses and workshops to help educators deepen their understanding of PBL and develop practical project design skills.
Guides and Templates:
- BIE Project Planner: A step-by-step guide for designing and implementing PBL projects, complete with templates and examples.
Books:
- “Project Based Learning Handbook: A Guide to Standards-Focused Project Based Learning for Middle and High School Teachers” by Thom Markham
- “Setting the Standard for Project Based Learning: A Proven Approach to Rigorous Classroom Instruction” by John Larmer, David Ross, and John Mergendoller
- “The PBL Playbook: A Guide to ACTIVELY Engaging Your Students in Real-World Learning” by AJ Juliani
Communities and Forums:
- PBL Network: An online community where educators can connect, share ideas, and collaborate on PBL projects and strategies.
- Twitter: Follow hashtags like #PBLchat and #PBL to join discussions and connect with educators passionate about PBL.
Educational Organizations:
- International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE): Offers resources and conferences focused on innovative teaching methods, including PBL.
- National Association for Gifted Children (NAGC): Provides resources and insights on using PBL to engage and challenge gifted learners.
Tips for Implementing Project-Based Learning For Schools:
- Clear Objectives: Define learning goals and objectives that align with the curriculum and desired outcomes
- Supportive Environment: Create a safe space where students feel comfortable taking risks and sharing ideas
- Guided Independence: Provide guidance and support while allowing students autonomy in project decisions
- Varied Resources: Offer a range of resources—books, articles, videos—to support research and learning
- Assessment Variety: Incorporate self-assessment and peer assessment to encourage reflection and growth
- Adaptation: Tailor projects to cater to diverse learning styles, abilities, and interests